[Macromolecular Chemistry and Physics]Strong Memory Effect of Metastable β Form Trans-1,4-Polyisoprene above Equilibrium Melting Temperature
Prof. Li and Dr. Lu et al. investigate the memory effects of α-TPI, β-TPI, and mixed α/β-TPI by means of differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), micro-Fourier transform infrared (MFTIR) spectrometer, and polarized optical microscope (POM). The related work is published in Macromolecular Chemistry and Physics (2017, 218, no. 20).
The memory effect of metastable β form crystals of trans-1,4-polyisoprene (TPI) is investigated with its thermodynamically stable α-TPI as reference. Unexpectedly, β-TPI exhibits a stronger memory effect over α-TPI. The memory temperature of β-TPI can be 20 °C higher than its equilibrium melting point (78 °C), while α-TPI has lost memory below the equilibrium melting point (87 °C). Moreover, the ordered structures in β-TPI memorized melt accelerate spherulite growth, and the growth rate depends on melting time, similar to previous mesomorphic isotactic polypropylene studies, implying metastable phase may have universal memory effects: wide memory temperature range, crystal nucleation and growth accelerating. The higher memory temperature of metastable phase may be from weak entropic difference with isotropic melt, which cannot overcome the barrier from entanglements as thermodynamically stable phase, leading to slow relaxation. This discovery can regulate crystalline morphologies of polymers by controlling the locations of different form crystals.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51325301, 51227801, 51633009, and 51303166).
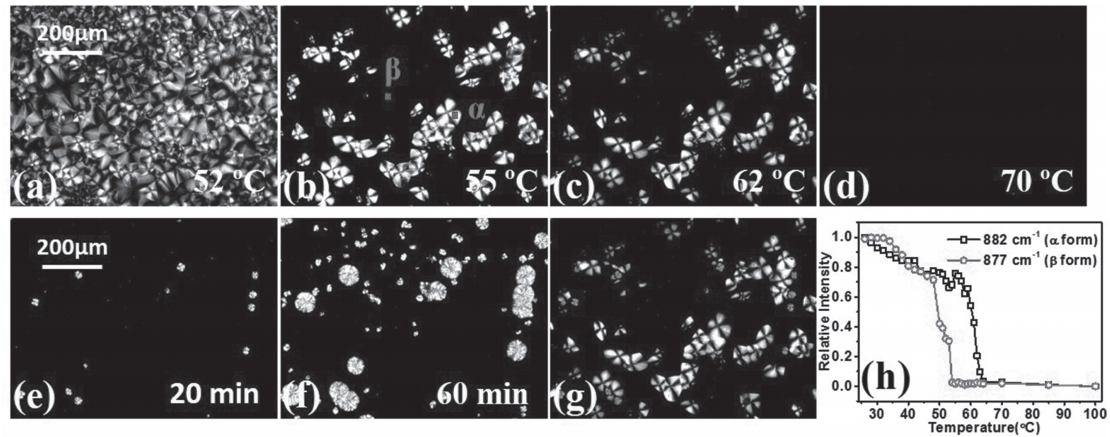
Micrographs of mixed α/β-TPI film during a–d) heating process from 25 to 100 °C and e,f) isothermal crystallization at 40 °C for different time after melting at 100 °C for 1 min. g) A combined micrograph of (c) and (e). h) The temperature dependence of relative absorbance intensity change of band 882 cm−1 (α form) and 877 cm−1 (β form) obtained by in situ MFTIR spectrometer. The measured areas are indicated by two red squares in (b).


