Recently, our research group published an article entitled ‘A hybrid adaptive element phase‐field method for quasi static and dynamic fracture’ on IJNME, and our doctoral student Tian Fucheng became the first author of the paper.
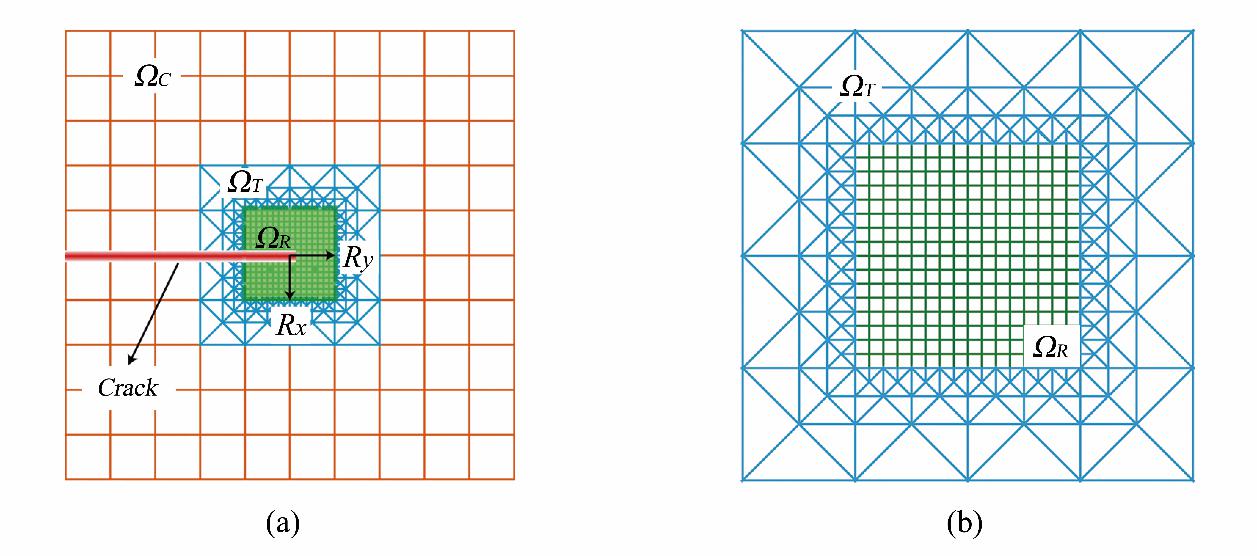
The present work aims at proposing a novel hybrid adaptive phase field method (ha-pfm) to solve various brittle fracture problems. The two key components of ha-PFM are refinement domain identification and multilevel hybrid adaptive grid algorithm, in which refinement regions are identified by digitally tracking approximate locations of crack tips based on the innovative strategy proposed in this work. As cracks propagate, the refinement domain moves dynamically, through adaptive mesh refinement, coarsening, and transformation strategies. Different from the previous adaptive finite element phase field method, we use adaptive multistage mixed triangular and quadrilateral elements to discretize the whole calculation. Only the transition areas connecting the fine and rough areas are discretized by triangular elements, which eliminates hanging nodes and ensures the high isotropy of the mesh near the crack tip. In addition, numerical results show that ha-PFM can significantly save memory and is 15 to 30 times faster than standard PFM without loss of accuracy. A schematic of a hybrid adaptive grid is shown below.
The author would like to thank professor Shen Yongxing (Shanghai Jiaotong university) for his guidance on numerical algorithms. This work is supported by key scientific research tasks of Ministry of Science and Technology (2016YF0302500) and national natural science foundation of China (51633009,51790500).
Related links:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/nme.6172


