Under the joint supervision of Researcher Liangbin Li and Postdoctoral Fellow Jungeng Chen, Ph.D. student Xueqing Han and colleagues from our team have innovatively proposed a new approach for synergistically modulating the optical properties of polyvinyl acetal (PVAc) films through molecular side-group chemical modification and sequential biaxial stretching.
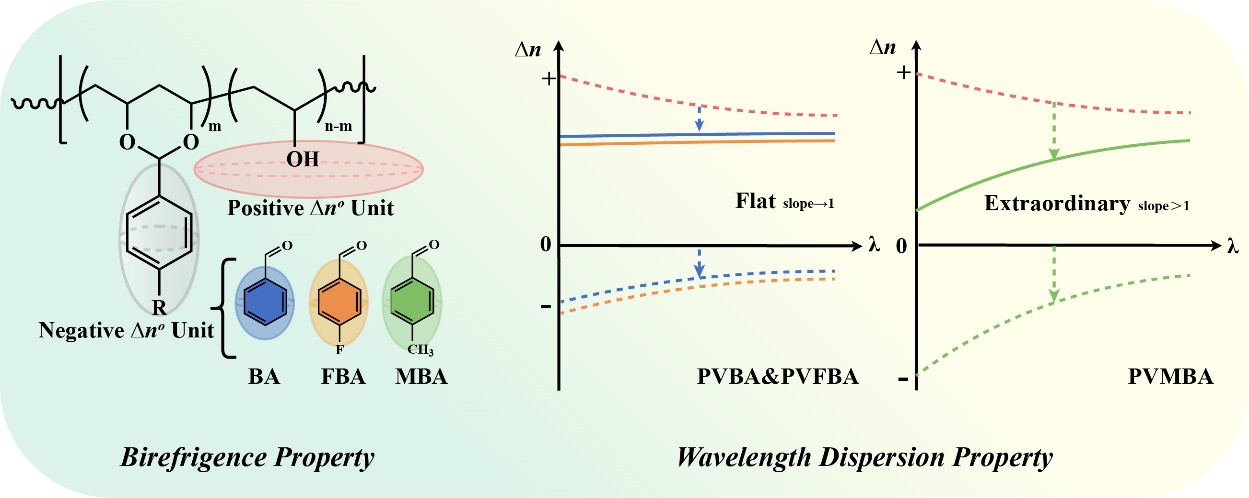
By conducting acetalization reactions between polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and benzaldehyde (BA), para-fluorobenzaldehyde (FBA), and para-methylbenzaldehyde (MBA), the team successfully synthesized a series of PVAc derivative films—namely PVBA, PVFBA, and PVMBA. During the biaxial stretching process, they revealed for the first time a three-dimensional refractive index modulation mechanism driven by the cooperative alignment of the polymer main chain and the molecular side groups.
This work addresses a long-standing challenge in PVA-based optical materials, where the high positive intrinsic birefringence of the hydroxyl groups limits tunability through mechanical deformation. By precisely introducing benzene ring substituents (–H/–F/–CH₃) with negative intrinsic birefringence and tuning the degree of acetalization (30%–50%), the team achieved a molecular-level dynamic balance between the positive birefringence of hydroxyl groups and the negative birefringence of aromatic rings.
In addition, the films overcome the limitation of conventional wavelength dispersion in PVA films: PVBA and PVFBA exhibit remarkably flat dispersion curves with slopes close to unity, while PVMBA displays anomalous wavelength dispersion behavior. The subsequent sequential biaxial stretching process enabled precise control of the internal two-dimensional stress field, leading to the synchronized modulation of main-chain orientation and side-group alignment in three-dimensional space. After stretching, the films exhibit anisotropy with nx>ny>nz, meeting the optical compensation requirements for VA-LCD display applications.
Polarized infrared spectroscopy confirmed that this optical anisotropy arises from strain-induced planarization and reorientation of molecular chains under biaxial tension.
This research has been published in the journal ACS Applied Polymer Materials and was supported by the Institutional Platform Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (JZHKYPY-2021-04).
Han X, Tan Z, Fang X, et al. Modulating Birefringence and Wavelength Dispersion of Biaxially Stretched Poly (vinyl acetal) Films[J]. ACS Applied Polymer Materials, 2025, 7, 8, 4992–5002
Paper link: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsapm.5c00216


